Where Visibility Meets Success
The timeline varies depending on the complexity of the project. Simple projects may take a few weeks, while more complex ones could extend to several months. Timelines are influenced by factors like scope, feedback iterations, and client responsiveness.
Project timelines vary based on complexity and scope. Small projects may take a few weeks, while larger ones could span several months. Timelines are established during project kickoff. We use a range of industry-standard tools such as Sketch.
- Service Category: Rubix Carabil Tower
- Clients: David Malan
- Project Date: 13 June, 2020
- Avenue End Date: 22 July, 2023
- Locations: NewYork - 2546 Firs, USA

Services Benefits:
We can do both. We can adhere to existing brand guidelines, ensuring consistency, or help develop new ones if a client is looking for a fresh identity. Our goal is to align the UI/UX design with the brand's overall strategy product meets the needs.
- We use the latest diagnostic equipment
- Automotive service our clients receive
- We are a member of Professional Service
- Digital how will activities impact traditional
- Architect and technical engineer


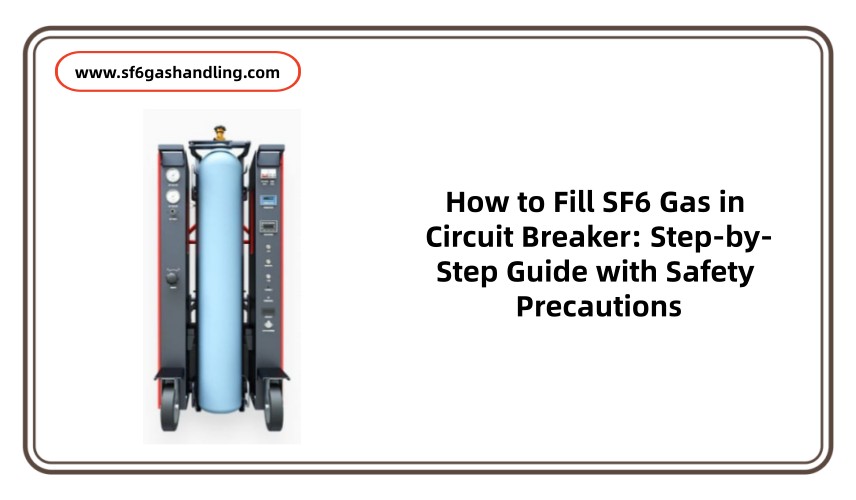

SF6 Gas Purification and Treatment System: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Solution
SF6 Gas Recycling and Reuse Solution: An Electrical Maintenance Solution that Meets Environmental Standards and Cuts Costs by 40%
SF6 Gas Recovery in High-Voltage Substations: A Guide to Efficiency & Sustainability